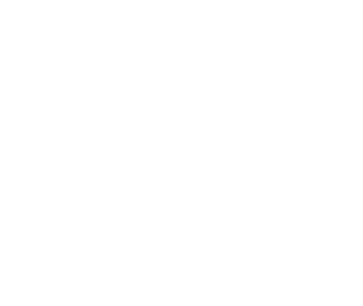


Chest pain can happen for a number of reasons that could be associated with your heart, lungs, or the digestive system. Some of the causes of chest pain can be life-threatening, whereas others can point towards a non-life-threatening condition. In the event when the cause of the chest pain is a heart issue, it can become fatal if no action is taken immediately. Therefore, whenever you feel sharp chest pain, you should consult a medical professional to rule out any life-threatening conditions. A specialist doctor may carry out investigations which may include a cardiac CT scan to diagnose the condition correctly and start the appropriate treatment.
Sudden onset of chest pain when breathing that goes away quickly can be caused by a number of factors. Chest pain can be described as either a stabbing pain like an electric shock, burning sensation, dull, squeezing, and pressurising. In any case, it may be caused by any of the following reasons:
Heartburn is a very common cause of chest pain. When the acid in the stomach splashes up into the oesophagus, it can cause chest pain or a burning sensation in the chest.
If the bones or muscles in your ribcage get injured or strained during any high impact activity like working out, injury, or a fall, it can cause sudden pain in the chest. If the muscle or bone irritates an adjoining nerve, it can cause chest pain.
Precordial Catch Syndrome refers to a condition where a nerve in the chest gets pinched or a chest muscle spasms, resulting in sudden sharp pain in the chest. This is a harmless condition that is usually common among children and young adults, however any person can experience it.
Anxiety and panic attacks can cause sharp pain in the chest and tightness that may also be mistaken for a heart attack. Individuals suffering from anxiety may experience such sudden pain or discomfort after a stressful event.
Chest pain is also often caused by lung problems. Some of these conditions may be serious whereas others are not that serious but can contribute towards chest pains. These conditions include:

Chest pain caused by a heart attack is typically described as a dull, crushing pain or a feeling of tightness in the chest. The pain may continue and worsen with time or it may last for a few minutes and then go away, only to return again later.
There are 2 distinct types of chest pain in patient with coronary artery disease. The stable type is when the chest pain symptom is mainly related to exertion/emotional stress and can be relieved with rest. The unstable type is when the symptoms can happen at any time where the pain usually lasts more than 30 minutes and associated with other symptoms like shortness of breath, sweating and nausea.
Moreover, chest pain caused by a heart attack cannot be pinpointed to a specific location; patients often feel diffused and widespread pain all over their chest which may or may not travel towards their neck, jaw, and arms. Apart from a heart attack, other heart problems like angina and myocarditis can cause a sudden pain in the chest.
Some digestive system disorders can also cause chest pain such as gallstones, pancreas inflammation, muscle spasms in the chest wall, and swallowing disorders.
If you feel chest pain symptoms that resemble those of a heart attack, it is essential to immediately seek medical attention. Race towards the nearest hospital if you feel:
If you experience chest pain symptoms, your doctor may order a cardiac computerised tomography (CT) scan to diagnose its underlying cause. Let’s go into detail about a cardiac CT scan in Singapore.
Find out about the difference between MRI and CT Scans in this article.
A cardiac CT scan is a non-invasive imaging test that is performed to evaluate the heart and its surrounding muscles to check for any blockages or narrowing of the arteries. A cardiac CT scan machine works by using x-rays generated from multiple angles to acquire high-quality 3D images of the heart muscle and surrounding areas.
Sometimes, plaque and buildup of calcium and other substances can narrow or block the coronary arteries that can hinder the blood flow to the heart resulting in chest pain and heart attack. A cardiac CT scan can allow doctors to identify the location and extent of buildup in the arteries that can help them recommend a treatment plan for the patient.
A cardiac CT scan can be done with or without a dye contrast to better visualise the heart, vessels, and other structures. A cardiac CT is able to show the following structures in the form of high-resolution, 3D images:
There are several benefits of a cardiac CT scan including the following:
A cardiac specialist may order a cardiac CT scan in Singapore for the following reasons:
Another diagnostic tool that is used to identify the cause of pain in chest or other heart issues is an angiogram. A CT coronary angiogram is a minimally invasive procedure that is used to visualise the heart muscle and view the blood vessels to check for any blockage. During an angiogram, a long hollow tube called a catheter is inserted into a large artery, usually in the groin or wrist. A contrast dye is then inserted through the catheter that can highlight the targeted areas. Fluoroscopy x-rays are used to assess the blood flow through the coronary arteries by taking images through several angles.
Although a minimally invasive procedure, there are several advantages of a conventional angiogram.
An angiogram is usually performed when there are symptoms such as chest pain that is highly suspicious of coronary heart disease. If your cardiac doctor suspects blockage or narrowing of the blood vessels of the heart, he may order a conventional angiogram for a more detailed diagnosis. An angiogram is also more effective in assessing the extent of narrowing in coronary artery blockage.
In case of CT Cardiac Scan versus Angiogram, both are diagnostic imaging tests to view the heart muscles, valves, blood vessels, and surrounding structures. However, there are a few differences between the two procedures and one might be more effective in some situations than the other. This comparison is discussed in the following points:
Depending on the underlying cause of chest pain, the doctor may recommend the following treatment options.
The following medications may be prescribed depending on the underlying cause:
Switching to a healthier lifestyle is essential to reduce the risk of coronary heart disease. Exercising regularly, eating a well-balanced diet, avoiding fats and sugars, stopping smoking, and maintaining good mental health are some lifestyle changes that can help prevent heart and other problems that may contribute towards chest pain.
In severe and life threatening causes of chest pain, a specialist doctor can recommend any of the following surgical procedures:
Chest pain can be caused by several factors, some of which may be life threatening. In case of any kind of chest pain, it is advised to visit your nearest medical service provider and get evaluated for the underlying cause. Most of the life-threatening causes of chest pain can be confirmed or excluded through a cardiac CT scan. For CT cardiac scan in Singapore and other diagnostic imaging tests, contact RadLink today and get specialised innovative care and assessment.
Usually a heart problem manifests itself in the form of chest discomfort, pressure, tightness, fullness, crushing pain, and burning in the chest that may spread towards the back, neck, jaw, and arms. Nevertheless, no type of chest pain should be ignored and medical advice should be sought immediately.
In case of any type of chest pain, visit a healthcare professional at the earliest.
The risks associated with CT cardiac scans are very less with a rare occurrence. These risks can include radiation exposure, allergic reaction to the contrast dye, and the dye leaking into the skin.
Consider the following suggestions for a cardiac CT scan preparation :
The images from the CT scan are ready soon after the scan. The technician will prepare the report and send it to your healthcare provider. If your arteries and heart look normal in the cardiac CT scan results and your calcium score is zero, these are considered normal results indicating that you do not have heart disease. Abnormal results may be indicated by a large calcium score, narrowing of the arteries, malfunctioning of the valves, inflammation or fluid in the heart, and tumours. Your healthcare provider will discuss the CT scan results with you and recommend treatment options accordingly.
Yes, a CT cardiac scan may be recommended for people with a high risk for heart disease since a CT scan is able to detect damage or blockage in the arteries in some cases even before there are any visible symptoms.